 Domino Data Lab provides a Data Science platform that empowers organizations to drive their business through the use of predictive models. The platform accelerates breakthrough research and increases collaboration and productivity of data scientists. The company was founded in 2013 and is based in San Francisco.
Domino Data Lab provides a Data Science platform that empowers organizations to drive their business through the use of predictive models. The platform accelerates breakthrough research and increases collaboration and productivity of data scientists. The company was founded in 2013 and is based in San Francisco.
Organizations can use Domino Data Lab on-premises or in the cloud, and its open platform supports both open source and proprietary tools and languages like Julia, Matlab, Python, R, SAS, and others.
When asked about the origins of Domino Data Lab, Co-founder & CEO, Nick Elprin replied:
“My co-founders and I started Domino because we saw more organizations, more companies, investing in Data Science without knowing how to get the most out of that investment. We aim to spread best practices that will make Data Scientists more productive, increasing their collaboration, scalability, and output.”
The Strengths of the Software
In a recent DATAVERSITY® interview with Elprin, he remarked:
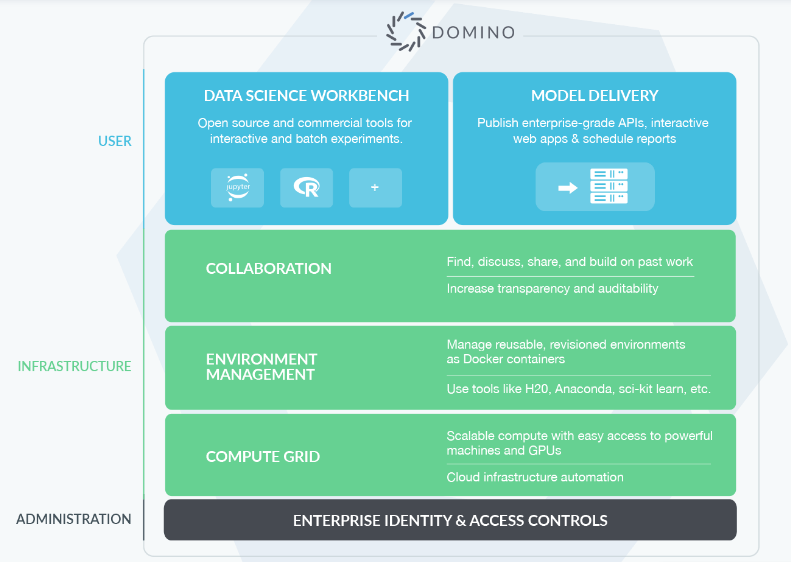
“Our software platform does three things that are all tightly integrated. The first is, we provide what we call a workbench, and that is a way of making Data Scientists more productive by letting them develop models and run computational experiments without having to deal with DevOps or infrastructure headaches and hurdles.”
With Domino, Data Scientists can easily run many simultaneous experiments with only the push of “one button,” said Elprin. It allows them to save time and effort usually spent on configuring machines and tracking their work. “We provide easy access to cutting-edge new hardware like GPUs,” as well as the latest Data Science tools.
In terms of the Cloud, Domino’s software provides a multi-tenant Cloud model that integrates with an organization’s private Cloud, Amazon’s Virtual Private Cloud (VPC), and others.
The second piece of the platform enables model delivery, accelerating the last mile of Data Science. Elprin added:
“So, the Data Scientists build a great model, but it takes nine months to get integrated into the production process, and then there’s no business value from it. We help solve that problem.”
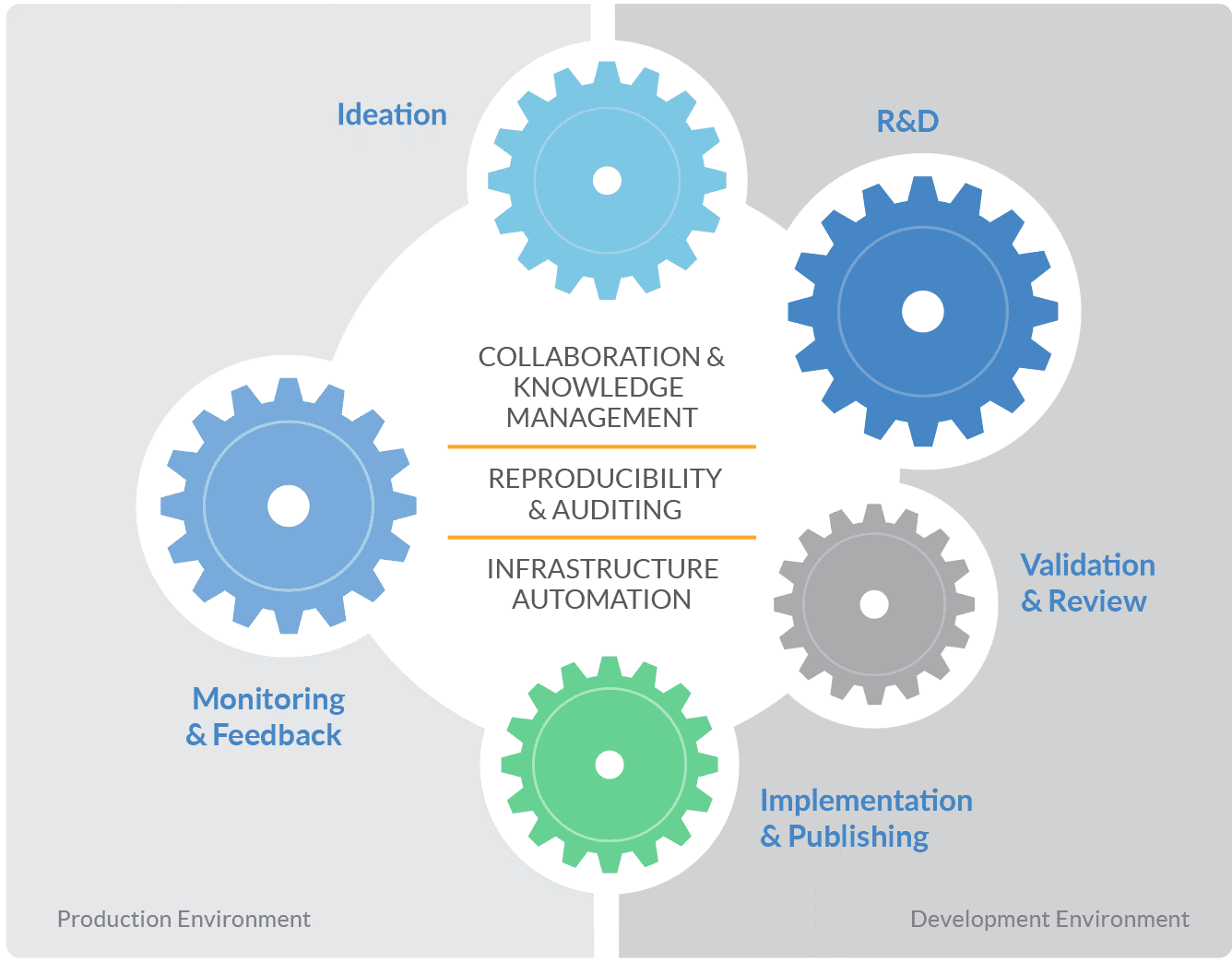
The final part of the platform is the Collaboration Hub. It sits underneath the Workbench and Delivery modules. As Data Scientists work, “our collaboration hub tracks everything they do, so it tracks the artifacts, the experiments, the results, the models, the codes that people run, the datasets they use,” said Elprin. It makes their work “searchable, discoverable, reproducible, reusable, and discussable.” As teams grow, it helps new users “build upon past work instead of reinventing the wheel.”
The ability to scale a team out is really a key component of the entire platform. It keeps Data Scientists and their teams from “bumping into each other or duplicating effort.”
Domino’s Ecosystem Partners Provide Services
Domino Data Lab has a growing ecosystem of partners, which helps their customers speed up the creation and delivery of strong, useful models. This significantly improves the productivity of Data Scientists, removing bottlenecks from the Data Science cycle. These partners include:
- SAS: Offers Analytics, Business Intelligence, and Data Management solutions by way of their software and services.
- AWS: Amazon Web Services is a comprehensive and broadly used Cloud platform.
- Trifacta: Offers “Data Wrangling” software to explore and prepare diverse datasets.
- DataRobot: Provides the experience, knowledge, and best practices of leading Data Scientists, delivering automation and easy-to-use Machine Learning initiatives.
The Models Make Automated Decisions
Domino Data Lab’s software supports the concept of automated decision making. For this to work, the model must be integrated into the existing data technology systems. Elprin described the uses and potential of this decision-making ability:
“This is also leading to entirely new kinds of products and services, and even kinds of business models. Instacart is successful because of the efficiency they’ve gained through model-driven automations. There are many more examples as well.”
He also gave the example of insurance companies and how people in car accidents can now just text a photo of the accident, rather than a claims adjuster having to go out in the field. It allows people to get automatic damage estimates and according to Elprin is “disrupting the way that traditional organizations do business.”
The Open Approach Philosophy
Domino Data Lab uses an “open approach,” which lets users choose from the great variety of open source and proprietary tools available for data research. Domino’s Compute Environment allows clients to easily try out new packages, without damaging other people’s workspaces or production models. Researchers can experiment, and reproduce their ideas and results without fear. Compute Environments can also be integrated with package management tools, such as Anaconda, to provide an even more powerful set of features. According to Elprin:
“Probably the biggest, or certainly one of the biggest differentiators for us, is that our platform is open and therefore is language and tool agnostic. There are tons of innovation in the open source ecosystem around new Data Science packages and techniques available to work with.”
He mentioned projects such as TensorFlow, H2O, and Python. Domino Data Lab built their platform to allow Data Scientists to integrate with and use any of those projects within their environment.
“We give Data Scientists the flexibility to keep up with the latest and greatest technologies, tools, and packages. And our platform automatically embeds best practices for reproducibility and knowledge management that we talked about earlier. When we see other companies try to provide platforms or tools to do similar things, they are usually more constraining, and they usually restrict Data Scientists to a narrower, more limited set of tools.”
He discussed how there are numerous organizations in the market doing really good work with models, leveraging automated decision-making packages and many other technologies. But, also cautioned that there are so many tools available now that it’s necessary for organizations wanting to work with Data Science to actually take a “bit of a step back to figure out how to manage the risk and liability of these new things.”
Domino Data Lab for Social Benefit
Increasingly, organizations focused on social good are becoming interested in using Data Science to accomplish their missions. Simultaneously, a large number of Data Scientists have become interested in donating their talents to projects for social good. The University of Chicago’s Center for Data Science and Public Policy at University is assisting “Domino for Good” in creating the Data Science for Social Good Marketplace (DSSG Marketplace) and bringing groups with this goal together in a novel way.
The DSSG Marketplace is an online coordination center for volunteering Data Science work. It acts to complement existing programs, by using different tactics for coordinating Data Science and social good. The Marketplace is designed to be:
- Modular
- Asynchronous
- Distributed
- Collaborative
- Easily reproducible
Elprin invited anyone interested to join Domino Data Lab in developing this new space of collaboration.
Domino Data Lab is also running a new Data Science Leaders’ Summit called Rev, with a focus on best practices for helping Data Science Leaders to run Data Science as an organizational capability and deliver true value to their business. According to Elprin:
“There are not really many communities that are great for leaders of Data Science teams. There are opportunities for practitioners to connect, and while there will be a track dedicated to helping practitioners, this conference is aimed at current and aspiring Data Science leaders.”
Photo Credit: sdecoret/Shutterstock.com