Click to learn more about author Tejasvi Addagada.
There is no “one model fits all” for maturity assessment. Maturity assessment is a powerful technique that can be leveraged by organizations to help assess themselves against external and internal benchmarks. One can compare Division to Division, Function to Function and Firm to Firm by leveraging a maturity model.
Organizations are utilizing maturity models to assess their data capabilities, educate their employees, identify gaps and compare their progress against industry peers. Maturity assessments are usually used to provide demonstrable and auditable evidence to peers and market authorities on the adoption of Data Management best practices.
By aligning the data programs with industry best practices, a firm can establish a benchmark from which to develop and grow your program. A maturity model creates the opportunity for organizational data programs to align and demonstrate to the sponsors, the business stakeholders, the senior executives, and the oversight authorities as well as regulators that they are adhering to an industry best practice critical to building, sustaining and leveraging their data. By using the benchmark, the same can be mapped to existing regulations like BCBS, GDPR to build or improve on these capabilities.
If regular employees start reading an assessment report, they might get lost in verbiage, a couple of minutes, into the report. Rather than having the stakeholders go through the complete report, a quantitative assessment that says 2.5 against the maturity model can help them better understand where the organization or division stands.
Where to Get One?
If there is a maturity model already put for data capabilities, the same can be brushed and customized to make it more contextual and usable. The other options available are to pick any vendor published maturity assessment like Dattamza or the ones from EDM which might not require any customization.
When Should One Create a Maturity Model and How?
Creating and customizing a maturity model from a strawman is effort and time incentive. But, it creates a common framework with defined capabilities, an established agreed-upon lexicon, identified objectives and deliverables as well as a list of identified evidence-based artifacts.
A Data Governance Strategy defines how Data Governance initiatives are planned, defined, funded, governed and rooted in the grass roots of the enterprise. It also defines the business value needed to be realized from the outcomes on reaching specific milestones. The maturity model is a prime technique that showcases the evidence-based outcomes, if put to consistent use can assist you in the moving towards a data driven culture.
While performing a Data Strategy analysis, along with related dimensions like Data Quality, the current state of the organization is assessed by using techniques detailed below.
1) Questionnaires and surveys sent to relevant stakeholders based on the impact, Influence, Knowledge, Interest and Attitude towards Data Quality.
2) Facilitating workshops and focus groups, with executive teams and senior leadership to align with organizational goals and stakeholder needs. Cobit provides guidance on how the goal cascading and assessment against the goals can be done.
3) Meeting with functions that need alignment to the Data Governance program like Risk, Privacy, Security, Legal and Compliance which provide cross functional support.
Once the gaps are identified, capability maturity maps can be put with existing or additional capabilities like a need for “central data profiling service”, “data delivery service” that are required to realize required outcomes say, “Achieve 80% accuracy in CRM lead demographic data”.
A business capability analysis can also be performed where the target state capabilities are assessed for business Value, performance gaps in existing capabilities like technical metadata management and risks associated. These capabilities usually encompass people, process, frameworks, policy, data, technology and culture, outlined in the strategic and operational roadmaps.
How to Use the Feedback to Improve the Models and Assessment?
You can use the nuances from the strategy analysis, business capability analysis, Data Governance assessment plan and operating model Key Performance Indicators to continuously specialize the maturity model. As discussed earlier, there are external and internal benchmarking standards available in the industry that an organization can embrace. I have put a comparison on each of these models that can help you in your journey.
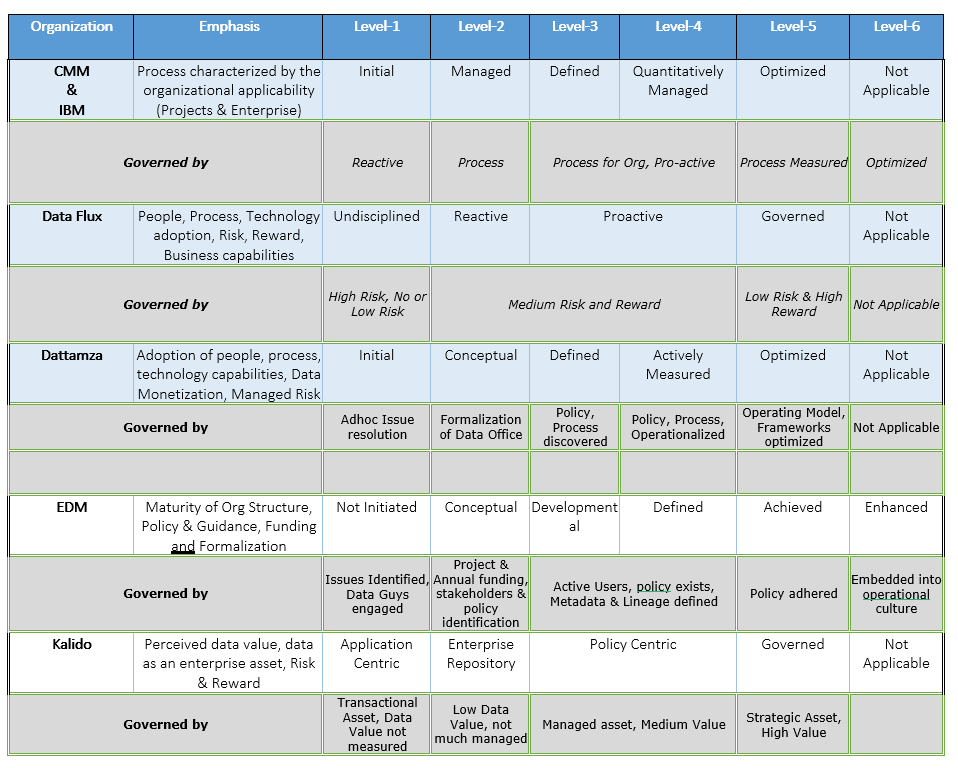
What Various Governance Models Emphasize on?
- Process and the nature of the outcomes with each achieved process state
- Adoption by People, Process and Technology
- Implementation of capabilities along with Risk and related Benefits
- Perceived data value from non-monetization to monetization data
- Data being traversed from being a transactional asset to an enterprise asset
- Implementation of Org structure, Policy, Lineage, Metadata, Funding, and Culture Change
- Effectiveness of Accountability, Formalization, Principles of managing and governing data
Overcoming Common Challenges
- The outcomes from the periodic maturity assessment should be used to assess the organization against a standard and agreed maturity model and outcomes.
- There should always be an alignment between the model principles and the principles based on which the organization goals are established.
- The maturity model on publication in the Enterprise, needs to be shared with the relevant stakeholders who have been a part of the assessment
- The assessment plan should have a combination of qualitative and quantitative assessment aspects.
- The maturity models need to be used at regular intervals to understand the gaps as per the strategy and roadmap and to look at the achievement of objectives.
- These gaps should be used as a feedback mechanism to Data Strategy analysis and planning.
- Change in strategic priorities, milestones and measures should reflect in the maturity model.
Firms are using maturity models to assess their data capabilities, educate their employees, identify gaps and compare their progress against industry peers. Maturity assessments are used to showcase demonstrable and auditable evidence to peers and market authorities on the adoption of Data Management best practices.
By aligning the data programs with industry best practices, a firm can establish a benchmark from which to develop and grow a data program. A maturity model creates the opportunity for organizational data programs to align and demonstrate to the sponsors, the business stakeholders, the senior executives, and the oversight authorities as well as regulators that they are adhering to an industry best practice critical to building, sustaining and leveraging their data. By using the benchmark, the same can be mapped to existing regulations like BCBS, GDPR to build or improve on these capabilities.